Data Management

Table Contents
We want transform data into information which can lead to business insights by taking data from multiple business functions to make useful and integrated. Now we are getting into the realms where many architecture solutions come into play to realize this. Irrespective of the architecture solution, there are key management capabilities each of them try to solve.
Collect
Source systems are typically designed for transaction processing and cannot curate, transform, or integrate data within themselves. We need to collect data from various sources, such as databases, applications, streams, or external sources, into a data platform for processing. This data is usually collected into cloud storage, which is partitioned into a separate layer of the larger data analytics architecture. This layer is what we call the raw layer and data is stored in it the original source system state.

The sub components to the collect architecture are below.
- Profile: Understand the source data’s structure and consistency so we can design and plan the data for analytics processing.
- Capture: Define, isolate and filter only the data which is required for analytics processing.
- Extract: Move the data from source system into the target system enviorment. (Usually On-prem/Cloud to Cloud).
- Load: Loading the data into the analytics processing system incrementally.
I get into more details about collect architecture in in this page.
Store
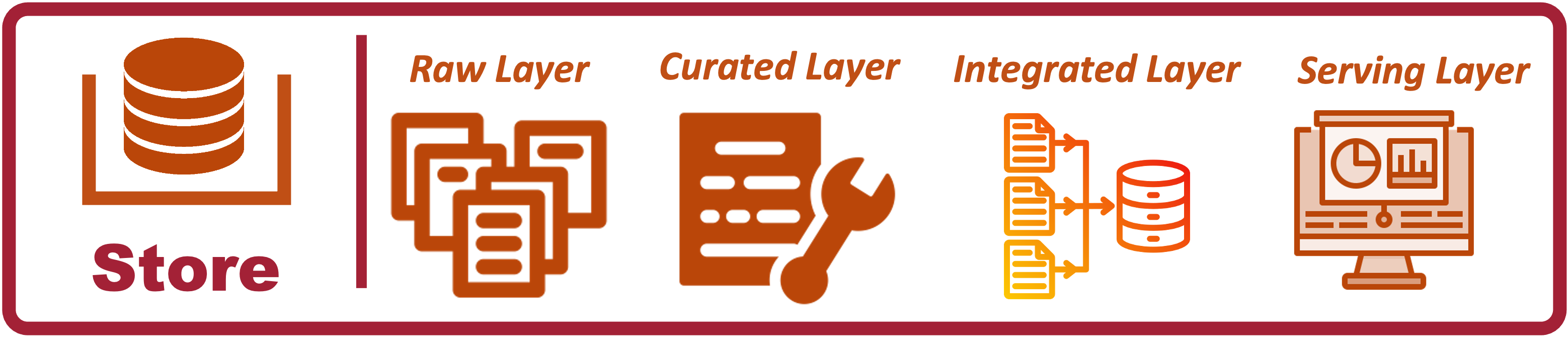
In a data analytics architecture, different layers are used to organize and process data as it moves from its raw form to its final, consumable state. Each layer has a specific role in the data pipeline, facilitating the transformation, enrichment, and preparation of data for analysis and reporting.
- Raw Layer: Stores unprocessed data exactly as it was received from the source.
- Curation Layer: Cleans, validates, and enriches data, making it consistent and reliable.
- Integration Layer: Merges, aggregates, and transforms data from different sources to create unified datasets.
- Serving Layer: Makes data available for consumption, optimized for specific use cases and end-users.
Curate
Data from source systems have multiple quality issues. One of the most important objectives of this stage is to improve the quality of the data so it is usable. I explain a simple process to achieve this below and explained in this page.
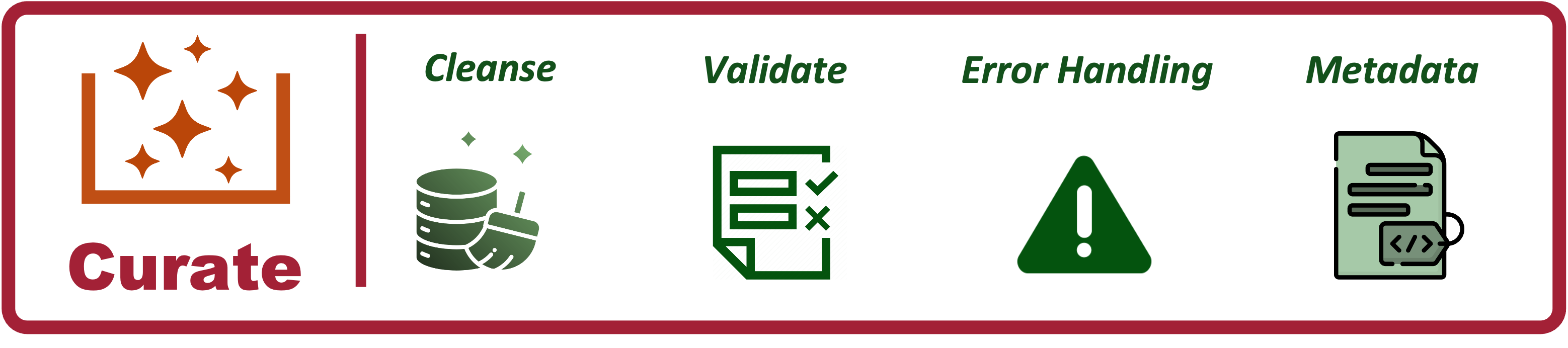
- Data Cleansing: Data cleansing, also known as data scrubbing, refers specifically to the process of detecting and correcting (or removing) corrupt or inaccurate records from a dataset. The primary goal of data cleansing is to improve data quality by fixing errors and inconsistencies.
- Validation: We also would need a process that ensures data is accurate and consistent to ensure it is usable so that it can be trusted by any consumers of the data.
- Error Handling: Fixing known errors in data (e.g., typos, incorrect values).
- MetaData:
Integrate
Coming Soon
Share
Coming Soon
Organize
Coming Soon
Describe
Coming Soon
Implement
Coming Soon
Related Pages
- https://nuneskris.github.io/portfolio/2-1-1CollectArchitecture
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/CollectDataProfiling
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/Collect-Data-Capture
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/Collect-Process-Pre-ingest-vs-post-ingest
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/Collect-ExtractLoad-Patterns
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/DataStore-RawLayer
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/DataAnalytics-Storage-2024
- https://nuneskris.github.io/portfolio/2-1-2CurateArchitectrure/
- https://nuneskris.github.io/publication/CurateDataCleansing
