Data: Warehouse, Lake and Lakehouse
I briefly referred to these three data architectures in the page where discussed about the history of analytics data architectures.
We will spend some more time to discuss the comparisons of these three data architectures as we use them in 2024.
Data Warehouse
- A data warehouse is a centralized repository designed to store structured data from various sources within the system and the data model is optimized for query performance via SQL.
- Since we have to load data into a model which is predefined (schema-on-write) data needs to transformed and cleaned before it is loaded (ETL - Extract, Transform, Load).
- The underlyting architecture is based on RDMS system which allows enforcing schema rules leading to consistency and integrity and there by enforces data consistency and integrity through ACID transactions.
- This means we can update existing data when there are chages to the data (CRUD) and expand the data we manage by expanding or evolve the schema.This allows strong data governance and quality.
- Business intelligence, reporting, and complex analytics are the main usecases of Data warehouses.
We have been building systems based on this architecture for more than 3 decades now and we know enough about it build integrated technologies, talent and development processes which ensures success. Snowflake brought life back into this architecture when organizations were either moving towards datalakes.
However they are very expensive to scale (Performance and data volume) and there was a high constraints on data neededing to be structured which required heavy ETL processes and development.
Data Lake
- There is a complete paradigm shift with datalakes. A data lake typically uses distributed storage like HDFS or Cloud storages.
- They can store vast amount of raw data in its native and diverse formats (JSON, XML, CSV) including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Rather than transform the raw data first and load data into a predefined schema, in data lakes we can ingest or laod data first in its raw form and then transform in a schema-on-read. We refer to this as ELT - Extract, Load, Transform).
- We are able to develop cost-effective storage solutions as we can use multiple commodity infrastructure using open storage format for this and thus are highly scalable to accommodate large volumes of data.
- Another interesting aspect of the technolgies which support this architectue is we can also scale compute when we need process the large data loads. By this decoupling of storage and compute we are not locked into having compute tied to the storage of system like legacy data warehouses.
- Data lakes support very diverese usecases such as big data analytics, machine learning, data exploration, and data science.
- We used Hive which was an SQL implementation on top of the datalake data. This was what I have seen most used. However, it was not perfect. When we had to update data, it was a nightmare and updating schema we had to recreate the entire dataset.
This freedom to dump data into the datalake led to oraganizations loosing control on what was loaded into the datalake with very limited management. This required robust data governance and metadata management which is often ignored.We term this situation as “data swamp”. Moreover the query performance is veruy slow compared to data warehouses.
However the biggest draw backs was there was a lack of schema evolution, lack of support to data updates and most importantly talent to build and support these systems were very expensive.
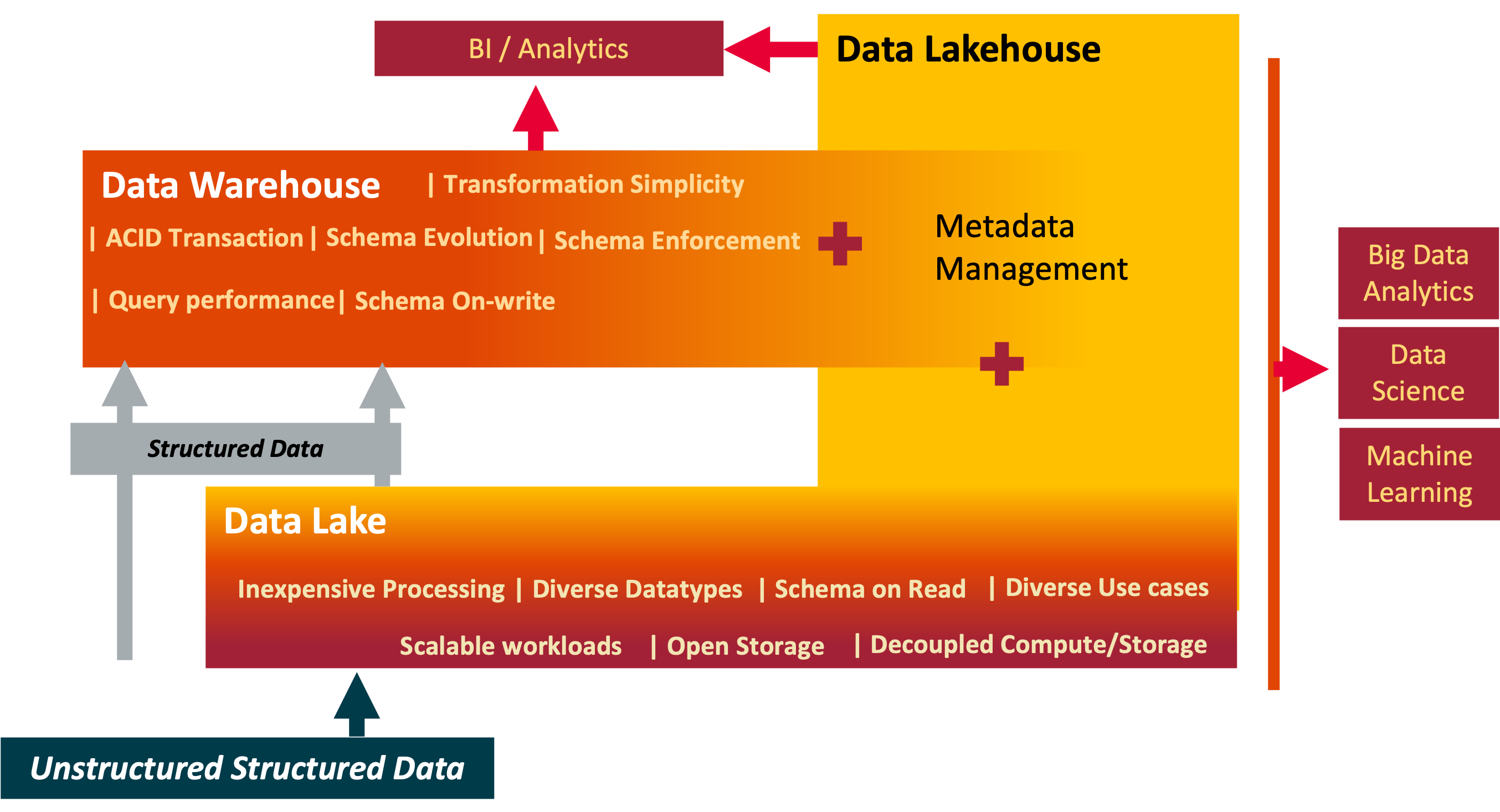
Data Lakehouse
- A data lakehouse is a modern data architecture that combines the best features of data lakes and data warehouses. It provides the data management capabilities and high performance of a data warehouse with the flexibility and scalability of a data lake.
- ACID Transactions are possible with modern table formats such as Iceberg, Hudi and Delta Lake. This ensures data consistency and reliability.
- The table formats allowed schema changes without significant disruption.
Summary of comparison
| Feature/Aspect | Data Warehouse | Data Lake | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Types | Structured | Structured, Semi-structured, Unstructured | All Types |
| Schema | Schema-on-write | Schema-on-read | Schema-on-read and write |
| Storage | Expensive, optimized for query speed | Cost-effective, scalable | Cost-effective, optimized |
| Performance | High | Variable | High |
| Data Processing | ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) | ELT (Extract, Load, Transform | ELT and ETL |
| Use Cases | BI, Reporting, Analytics | Big Data Analytics, Data Science | Unified Analytics, BI, Data Science |
| Data Consistency | Strong (ACID transactions) | Variable | Strong (ACID transactions) |
| Flexibility | Limited | High | High |
| Governance | Strong | Requires additional tools | Strong |
Conclusion
- Data Warehsourses are best for structured data and traditional business intelligence and reporting with high performance and strong data governance. Talent is available and outcomes are highly predictable.
- Data Lake are ideal for storing vast amounts of raw data in various formats, supporting big data analytics, data exploration, and machine learning. As long as we keep things simple, we can have successful outcomes.
- Data Lakehouse is very new and I will wait and see. But there is high excitement this architecture and I believe it is the architecture to consider now.
